Module 7 Office Hour: Callbacks, Async Programming, and Fetch
📸 Any questions over the module work?
🔁 Callback Functions
A callback function is a function passed as an argument to another function, to be "called back" later.
function sayHello(name) {
console.log("Hello, " + name);
}
function greetUser(callback) {
const userName = "Student";
callback(userName);
}
greetUser(sayHello); // Hello, Student
⏳ Callbacks and Async Programming
JavaScript is single-threaded, but it can appear asynchronous using the browser environment (Web APIs, event loop).
Example with setTimeout:
console.log("1");
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("2 (after 1 second)");
}, 1000);
console.log("3");
// Output: 1, 3, 2
Explanation:
- JS executes
console.log("1") and console.log("3") immediately.
setTimeout is handled by the browser's Web API and queued later.
Visualize the Call Stack + Callback Queue + Event Loop
You can visualize any async code using this visualizer!
Event Loop
This is an example of a scrollable document. Here's an embedded image for visual engagement:
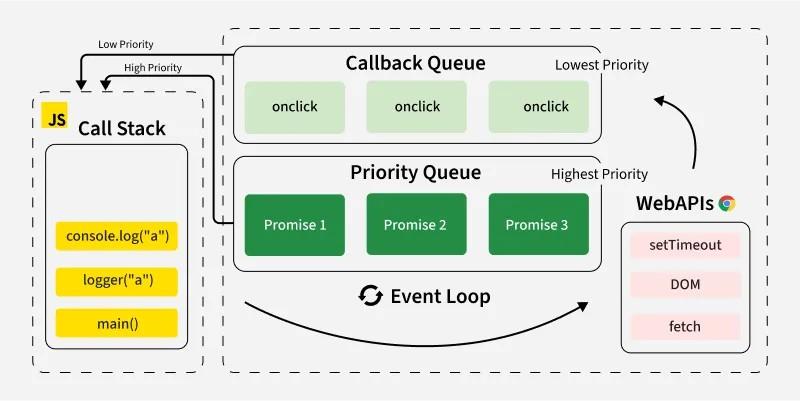
🔄 JavaScript Event Loop Explained
📋 Call Stack
Where synchronous code executes. Functions are pushed and popped in LIFO order (Last In, First Out).
🌐 Web APIs
Browser-provided APIs like setTimeout, fetch, DOM events that run outside the main thread.
⏳ Callback Queue
Holds callbacks from Web APIs, waiting to be executed when the call stack is empty.
🎯 Event Loop
Continuously checks if call stack is empty, then moves callbacks from queue to stack.
🔄 How It Works:
- Execute: Synchronous code runs immediately in the call stack
- Delegate: Async operations (setTimeout, fetch) are handed to Web APIs
- Wait: Web APIs process the operation in the background
- Queue: When complete, callbacks are added to the callback queue
- Loop: Event loop checks if call stack is empty, then moves callbacks to stack
🌐 Fetch in JavaScript
fetch() is used to make network requests. It returns a Promise.
fetch('https://api.openbrewerydb.org/breweries')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
console.log("Breweries:", data.slice(0, 5)); // Show first 5 breweries
})
.catch(error => console.error("Error:", error));
We'll use this in our office hour project next!
🚧 Office Hour Project: Brewery Finder
We'll build this step-by-step. Here's what we'll do:
- Let the user search for breweries by city or type
- Display results in a clean UI
- Practice using
fetch and dynamic DOM manipulation
We'll start this live in office hours — no code yet!
